guinea

guinea, AN OVERVIEW
With 13.1 million inhabitants, Guinea has seen sustained growth of its economy since 2016.
Sixty-five percent of the population lives outside of cities because of the important economic role played by agriculture and natural resources. The agriculture sector is the country’s leading employer and is key to alleviating poverty and rural development: it accounts for 57% of rural household revenue and 52% of the labor force.
Male-female inequality in education, access to work and access to decision-making posts remains a major challenge for the country. There are still major constraints: weak human capital (with low literacy rates), a poor health system, limited access to finance and high unemployment, especially among young people.
guinea IN FIGURES
- Total population * : 13.1 M
- Very young population* :
- 32% aged between 10 and 24
- 42% aged under 15
- Population growth rate* :
- 2,5% per year in Guinea
- 1,1% per year in global terms
-
Fertility rate of women aged 15-49 (2015-2020)* : 4,7 children per woman
-
Contraceptive prevalence rate of women aged 15 to 49 (2018)* :
- 8% all methods
- 10% modern methods
- Maternal mortality ratio (2017)** : 576 deaths per 100,000 live births
- Rate of early marriage* : 32% of adolescents aged 15 to 19 married
- Early pregnancies* : 58,1% of adolescents under the age of 19 pregnant or have given birth
- Unmet family planning need: 25% of women aged 15 to 49

GUINEE
THE FRENCH MUSKOKA FUND IN guinea
Read about some of our high-impact interventions:
The French Muskoka Fund as a leveraging tool and instrument of influence
In Guinea, complementarity of funding between the French Muskoka Fund and Mano River has had considerable leverage in the post-Ebola period. Developing protection kits for health care staff and a list of essential medical devices and equipment for managing patients affected by the 2015 Ebola epidemic have helped strengthen the resilience of the health system.
Also during the Ebola epidemic, activities to improve the quality of midwife care funded by the French Muskoka Fund complemented those undertaken by Japanese funds which, for their part, helped fund the reintroduction of some midwives into health facilities despite the risks incurred.
Improving Emergency Obstetric and Newborn Care
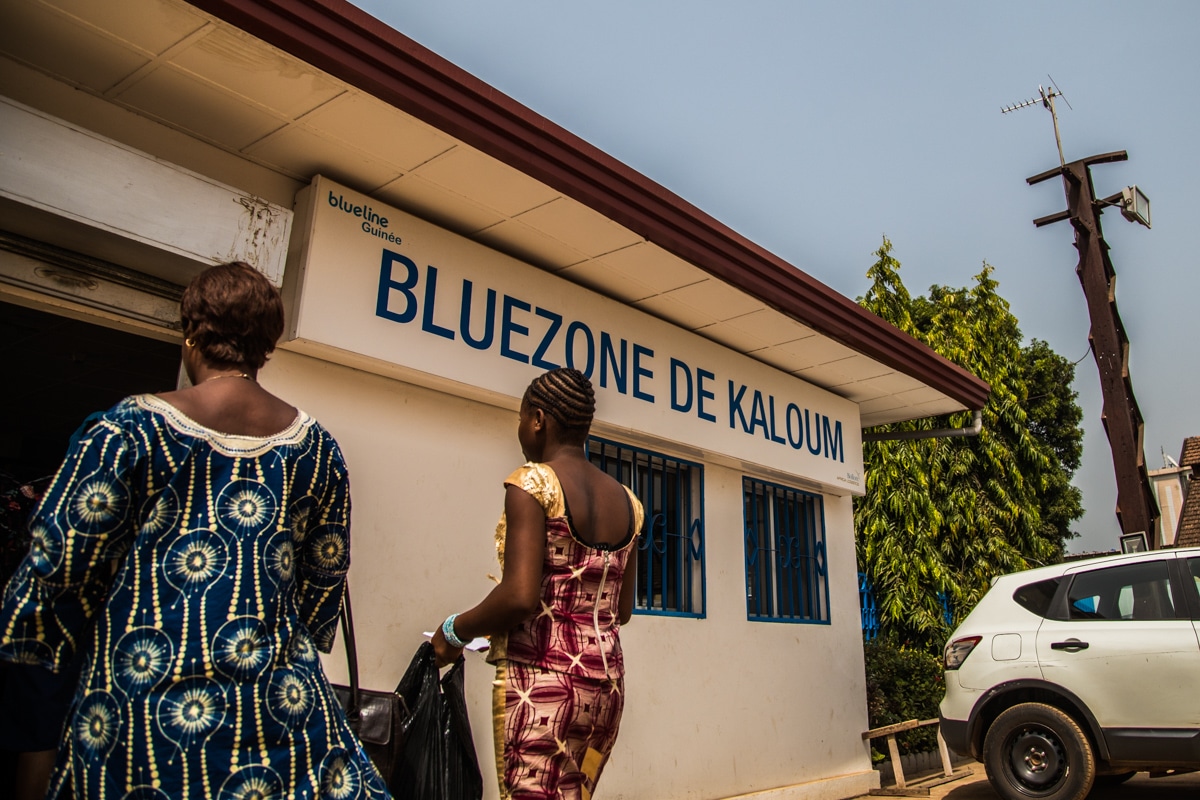

The number of health facilities qualified to provide BEmONC rose from close to zero in 2012 to 3 in 2013, 47 in 2014 and 72 in 2015.
In 2017, 34 BEmONC and 25 CEmONC services were fully operational.
As a result, the EmONC (Emergency Obstetric and Newborn Care) available in 2015 covered a population of 5.5 million inhabitants out of the country’s population of 10.6 million, in line with international standards.
Activities are continuing to make them fully operational.
Decentralized monitoring: locally accessible services for mothers and children
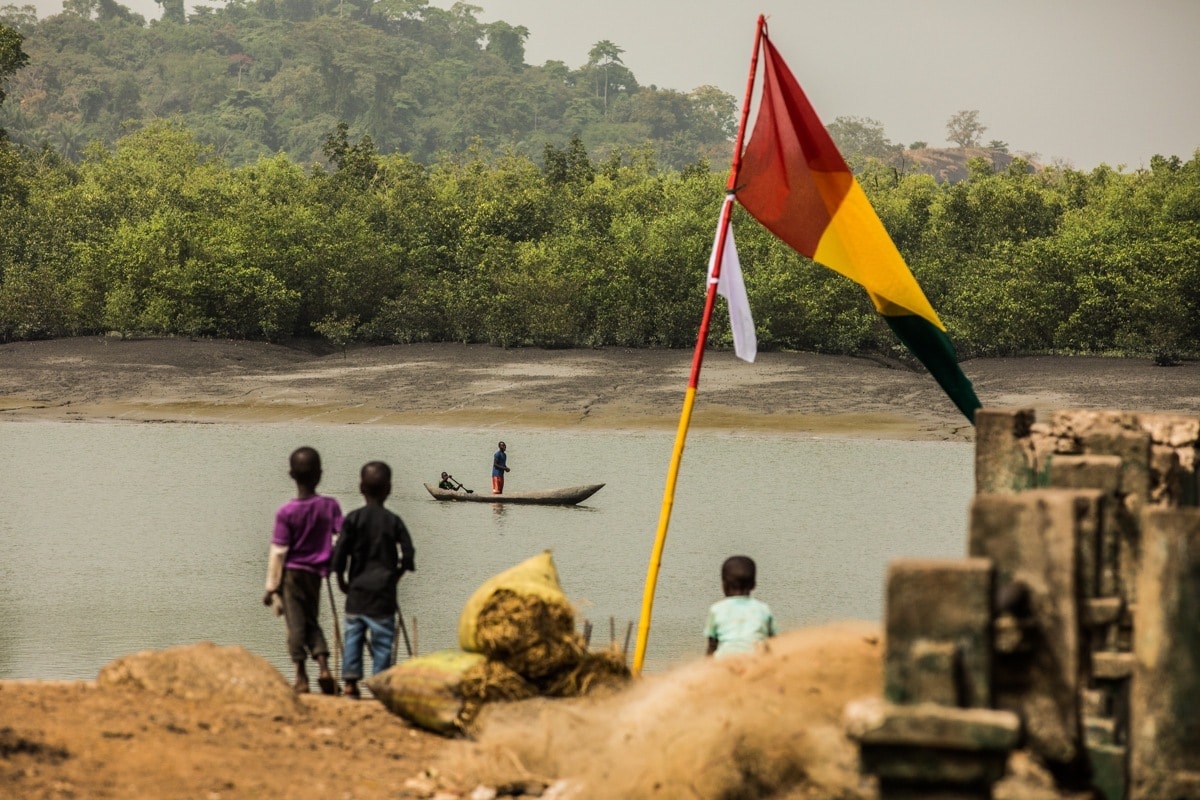

In Guinea, community-based delivery is ensured by the adoption of an integrated approach between the different mother and child health services.
This includes the integrated management of childhood diseases; vaccinations; family planning; nutrition; water; hygiene and sanitation; prenatal and postpartum consultations; gender-based violence/female genital mutilation; HIV; integrated disease surveillance and response, including community-based maternal and newborn deaths; and home-based newborn care.
This approach has been introduced in 750 villages in 11 prefectures (Labé, Mali, Koubia, Siguiri, Kankan, Mandiana, Kindia, Télimélé, Coyah, Forécariah and Dubréka) out of the 38 that make up the country.
Adolescent and youth sexual and reproductive health
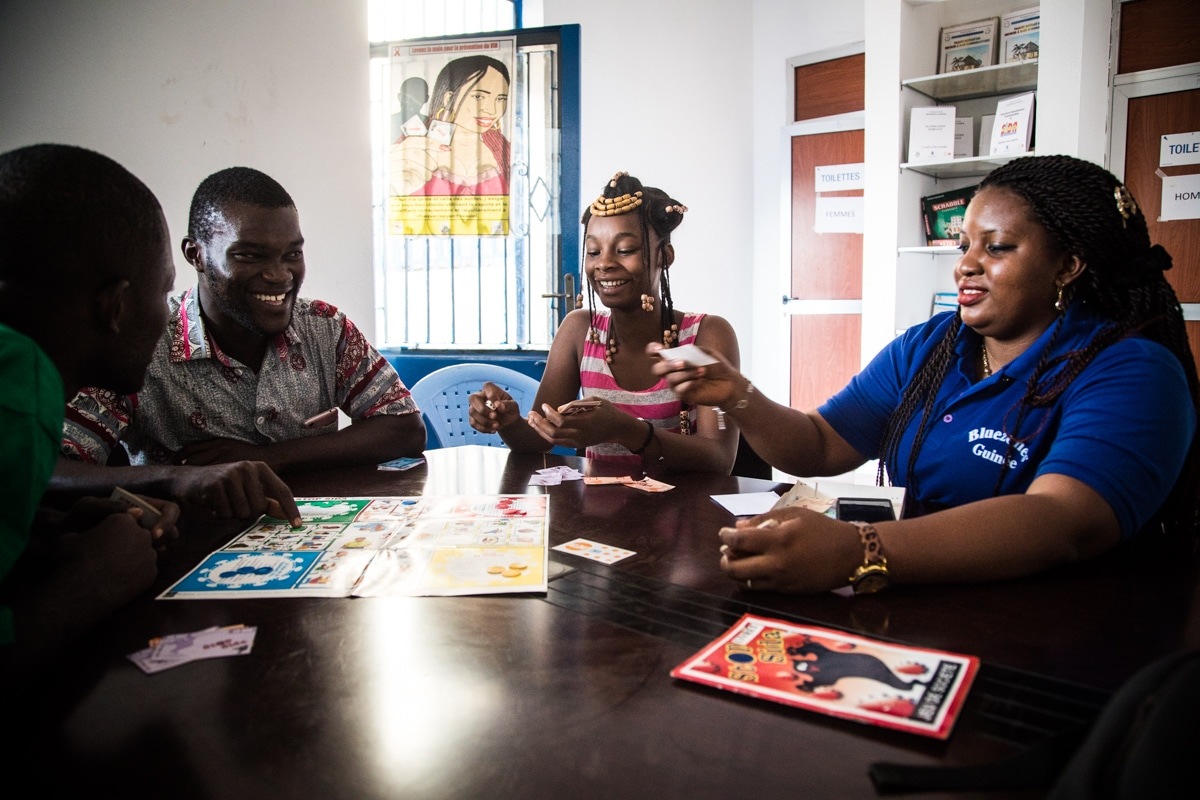

In Guinea, the availability of adolescent and youth sexual and reproductive health services has significantly increased since 2012, rising from 10 facilities providing SRH services for young people to 76 facilities in 2017. These services are provided in different types of facilities: public health facilities; health facilities managed by an NGO/CSO to create a welcoming space for adolescents and young people; and school and university clinics. Some services are also provided using advanced strategies such as family planning and HIV campaigns.
Activities that help these services become more effective include training management teams and service providers on AYSRH standards, supplying equipment and drugs and setting up welcoming spaces.
KEY RESULTS
%
reduction in newborn mortality between 1990 and 2018 in Guinea
%
reduction in under-five mortality between 1990 and 2018 in Guinea
%
increase in the rate of births attended by qualified staff between 2010 and 2017 in Guinea
%
increase in exclusive breastfeeding rates in babies under 6 months in Guinea
%
increase in women’s use of modern contraception in 2017 in Guinea
stories
Hadja
Conakry, Guinea
Fanta
Conakry, Guinea
Contact us
To contact us, complete the form below and we will get back to you as soon as possible.

